The number of critics of crisis-related austerity policies characterised by cuts in government spending and tax hikes is also on the rise. They argue that the focus of the debate in Europe on debt has stifled investment and economic growth unnecessarily, creating a legacy of missed economic opportunities and deteriorating or missing infrastructure. This has often had adverse unintended effects such as increased rather than reduced public debt, and may have a negative economic impact well into the future.
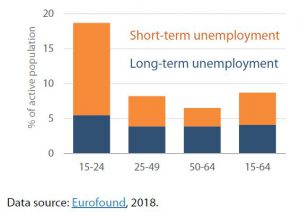
Even though employment and labour market conditions in the EU have improved since the crises, high youth unemployment in both the short and – particularly damaging – the long term remains a problem (Figure 4). The situation in several southern Member States is still worrying. The crises also caused an increase in income inequality across generations, between countries, and in some cases within countries, while income support systems are often insufficiently equipped to address this. Inequality has a negative impact on growth and is likely to fuel populism. In some Member States, while gross domestic product has grown, productivity and real disposable incomes have stagnated. This and austerity measures, including underinvestment in the public sector, have contributed to economic struggles for many voters, contributing in turn to the weakening of the centrist political parties in Europe. Some commentators see the need to focus on the economic and social status of ordinary voters who feel under pressure from globalisation, austerity and immigration. They recommend reassessing EU fiscal rules as the first step towards addressing the causes of rising political extremism.
Finally, upward convergence, which is one of the goals of the EU, has been negatively affected by the crises. Differences in income in the euro area’s founding countries has risen, while convergence has occurred in the new Member States only, casting doubts as to the robustness of economic integration in the Union. Social convergence has also been negatively affected with a widening gap between the most developed and the least developed countries in the Union.







Be the first to write a comment.