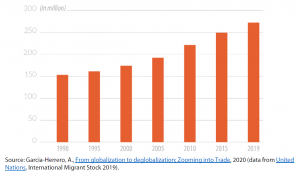
While international tourism represents a cross-border social exchange of a few weeks or months, migration usually implies a longer and often deeper social integration. In the slowbalisation period, international migration continued to grow in absolute terms, peaking in 2019. International mobility, whether for voluntary or humanitarian reasons, was on the rise. In addition to quantitative growth, the global governance frameworks for migration were also developed in the same period, running counter to the predictions of the slowbalisation assumption. In particular, the Global Compact for Safe, Orderly, and Regular Migration represents an ambitious plan to develop a normative framework for the multilateral governance of migration.
The annual growth rate of migration had already begun to slow after 2010. This is mostly due to increasing immigration restrictions introduced by various governments, which can also be attributed to the rise in anti-immigration political discourse. In the USA, for example, there was a rapid increase in visa denials. In Europe, a heated political debate on migration issues was ignited during the EU migration crisis and also featured strongly in the 2016 Brexit referendum. Since the immediate and ongoing consequence of Covid 19 pandemic measures was to close borders, this could strengthen the slowing trend in global migration.







Be the first to write a comment.