Written by Magdalena Pasikowska-Schnass and Philippe Perchoc,

The term Holocaust refers to the mass murder of 6 million European Jews, Roma and other persecuted groups, whom the Nazi regime and its collaborators sought to annihilate.
The expropriation, state-sponsored discrimination and persecution of the Jews by the Nazi regime began in 1933, followed by pogroms and their mass incarceration in concentration camps. Ultimately, this policy was extended to all Nazi-controlled European territories and countries during World War II, culminating in mass summary executions (‘Holocaust by Bullets’) and extermination in death camps. The perpetrators were prosecuted at the Nuremberg trials in 1945-1946; however, the tribunal preferred to indict them on charges of crimes against humanity rather than genocide.
It was not until 2005, on the occasion of the 60th anniversary of the liberation of Auschwitz that a United Nations resolution designated 27 January the day for international commemoration of the Holocaust, to be known as ‘International Holocaust Remembrance Day’.
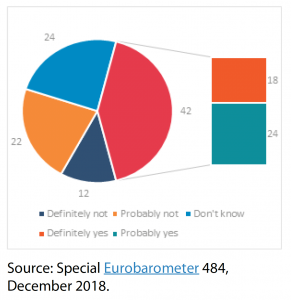
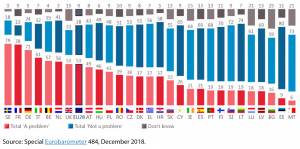
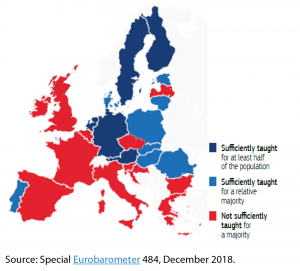
In the European Union, numerous programmes seek to preserve the memory of these tragic events in the history of the continent. Since 1995, the European Parliament has adopted resolutions drawing attention to the obligation to remember not only through commemorations but also through education. In November 2018, the EU became a permanent international partner of the International Holocaust Remembrance Alliance (IHRA).
Read the complete briefing on ‘The European Union and Holocaust remembrance‘ in the Think Tank pages of the European Parliament.








[…] […]
Prideparade mocks jews and the holocaust
https://www.dailymail.co.uk/news/article-8046043/Spanish-carnival-featuring-lingerie-clad-female-Nazis-sparks-fury-Jewish-groups.html?ito=amp_twitter_share-top